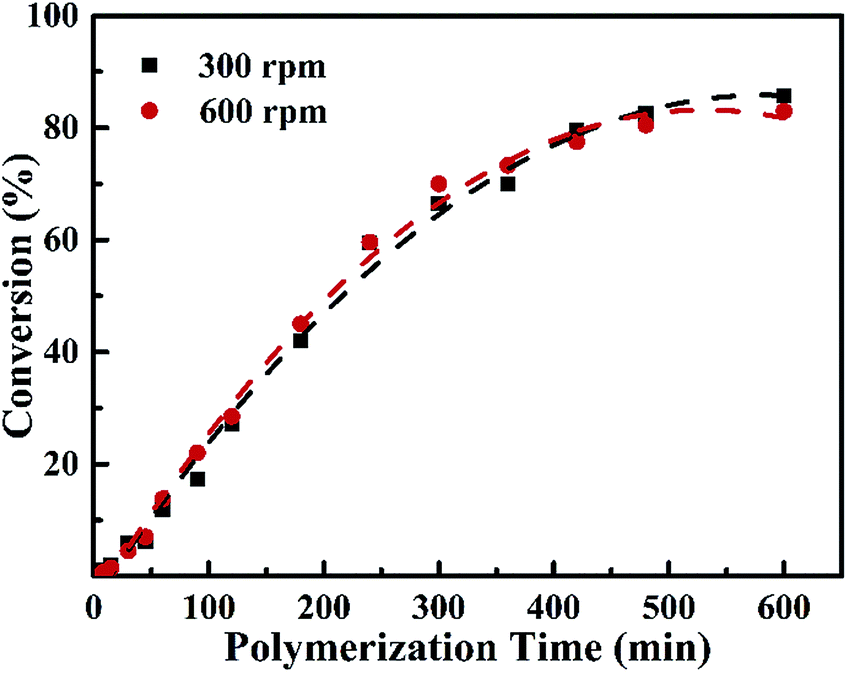
Vc vc α d 1 vc β β d 2 and vc d 3 were used to study the reactivities of the hydrogen atoms in the polymerization and the β hydrogen atoms contributed to the chain transfer.
Explain the polymerization of vinyl chloride.
About 80 of production involves suspension polymerization.
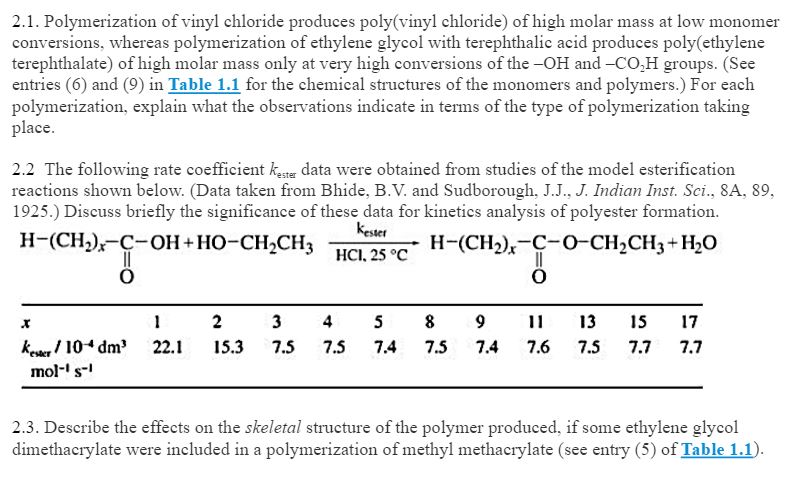
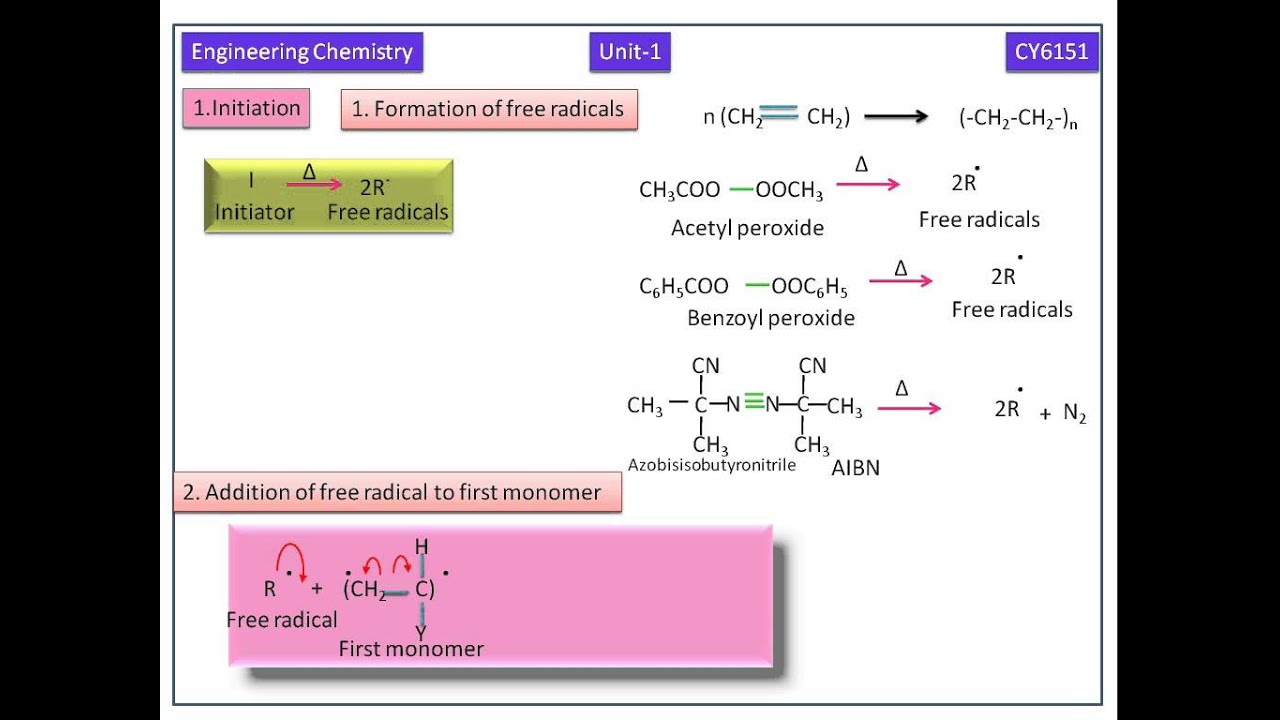
Free radicals can be formed by a number of different mechanisms usually involving separate initiator molecules.
Following its generation the initiating free radical adds nonradical monomer units thereby growing the polymer chain.
Polyvinyl chloride is produced by polymerization of the vinyl chloride monomer vcm.
The polymerization of vinyl chloride has been studied dilatometrically in chlorobenzene using azoisobutyronitrile as an initiator at temperatures between 30 and 45 c and with monomer and initiator concentrations varying from 1 0 to 8 1 m and from 0 005 to 0 1 m respectively.
The surfactant molecules composed of a hydrophilic water attracting and hydrophobic water repelling end form a stabilizing emulsion before polymerization by coating the monomer droplets.
Pvc vinyl chloride is an organohalogen compound that has important industrial applications.
Emulsion polymerizationaccounts for about 12 and bulk polymerizationaccounts for 8.
Emulsion polymerization accounts for about 12 and bulk polymerization accounts for 8.
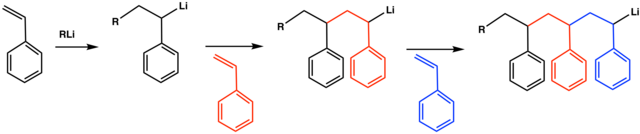
Addition polymerization of vinyl compounds or related unsaturated compounds as vinylidene chloride.
Molecular weights of the polymers have b.
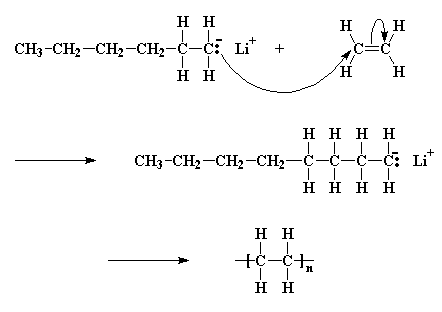
Thus vinyl acetate would be classed as an electron donor type monomer section 9 10 2 but it cannot be polymerized cationically because the carbonyl group complexes the active center.
Other surfactant molecules clump together into smaller aggregates called micelles which also absorb monomer molecules.
Definition of vinyl type polymerization.
A typical polymerization includes 180 parts water and 100 parts vinyl chloride monomer chain transfer agent trichloro ethylene.
Polyvinyl chloride is produced by polymerizationof the vinyl chloridemonomer vcm as shown.
When treated with certain catalysts vinyl chloride monomers undergo polymerization and form the larger compound known as polyvinyl chloride or pvc.
Pvc is used in the manufacture of numerous products including packaging films and water pipes.
The reactants are then heated in the closed system to about 50 c and the pressure rises to about 0 5 mpa.
For efficient cationic polymerization of vinyl monomers it is necessary that the carbon carbon double bond be the strongest nucleophile in the molecule.
About 80 of production involves suspension polymerization.